They record the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and other expenses incurred by the business. In financial accounting, bookkeeping is essential to keep track of the financial transactions of a business. One of the most important concepts in bookkeeping is the use of debits and credits. Debits and credits are used to record financial transactions in the accounting system. These accounts represent the cost of acquisition and amortization of these assets. The balance of these accounts decreases over time due to amortization.
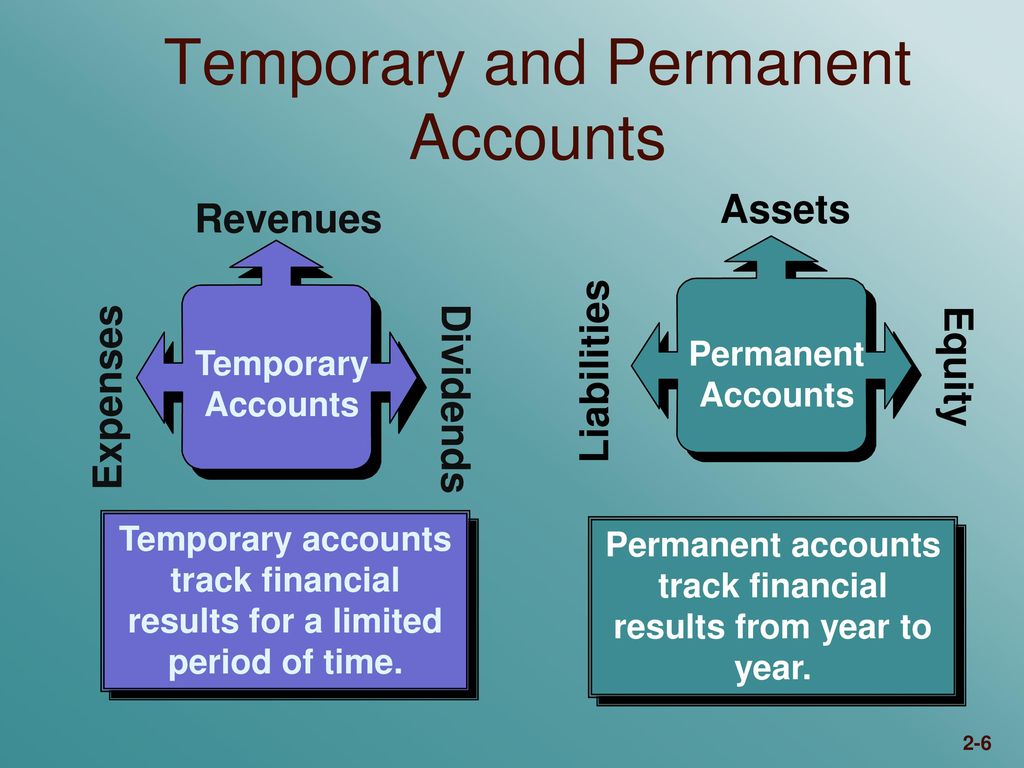
- A temporary account is an account that begins each fiscal year with a zero balance.
- The chart of accounts and sub-accounts are important tools for managing a company’s finances.
- Because you don’t close permanent accounts at the end of a period, permanent account balances transfer over to the following period or year.
- Basically, permanent accounts will maintain a cumulative balance that will carry over each period.
- Further, automation tools can enhance this process, ensuring sound financial management.
Natural Personal Accounts
This includes owner’s capital account in sole proprietorship, partners’ capital accounts in partnerships; and capital stock, reserve accounts, and retained earnings in corporations. This is in contrast to temporary accounts (like revenue, expense, and dividend accounts), which are cleared to Retained Earnings at the end of each accounting period. The income statement, also known as the profit and loss statement, shows a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period. It provides insight into the company’s profitability and helps investors and creditors assess its ability to generate income. To track revenue accounts, businesses often use accounting software or spreadsheets.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Calculating Interest Expense for Notes Payable
These accounts are also known as permanent accounts as they are not closed at the end of an accounting period. The balance of a real account is carried forward to the next accounting period. At the end of the accounting cycle, the income summary account is closed to the retained earning account. To determine if an account is permanent or temporary, check if it carries its balance over to the next period. Permanent accounts like assets, liabilities, and equity maintain balances across periods, while temporary accounts like revenue and expenses reset to zero at period-end. For temporary accounts, automation simplifies the process of closing and resetting balances at the end of each accounting period.
Common Challenges in Managing Temporary and Permanent Accounts
Permanent accounts are found on the balance sheet and are categorized as asset, liability, and owner’s equity accounts. A temporary account is an account that begins each fiscal year with a zero balance. At the end of the year, its ending balance is shifted to a different account, ready to be used again in the next fiscal year to accumulate a new set of transactions. Temporary accounts are used to compile transactions that impact the profit or loss of a business during a year.
There is no difference between income statement and profit and loss. The income statement is also known as statement of income or statement of operations.Income statement are actually the same, the terms will be used interchangeably throughout this article. Basically, to close a temporary account is to close all accounts under which of the following accounts are permanent the category. Accrued revenue—an asset on the balance sheet—is revenue that has been earned but for which no cash has been received. Businesses typically list their accounts using a chart of accounts, or COA. One of the most important aspects of nominal accounts is that they are closed at the end of each accounting period.
Capital and Investments
The traditional approach to accounting is known for its simplicity and ease of use. It provides a clear and concise way of recording financial transactions and provides a comprehensive view of a company’s financial position. The chart of accounts and sub-accounts are important tools for managing a company’s finances. They provide a clear picture of the company’s financial health and help to ensure that all transactions are properly recorded.
Liability accounts are used to keep track of these obligations and to ensure that the company is meeting its financial obligations. Nominal accounts are accounts that are used to record expenses, income, gains, losses, and other transactions that are not related to the purchase or sale of goods or services. These accounts are also known as income statement accounts or profit and loss accounts. Natural personal accounts are accounts that are maintained for individuals. These accounts include accounts of individuals such as John Smith, Jane Doe, and so on. Capital accounts – capital accounts of all type of businesses are permanent accounts.
These accounts are important for businesses because they help to measure the financial performance of the company. By tracking the money that is coming in, a business can determine whether it is profitable and make decisions about how to allocate resources. Liability accounts are used to track the company’s obligations to these creditors.